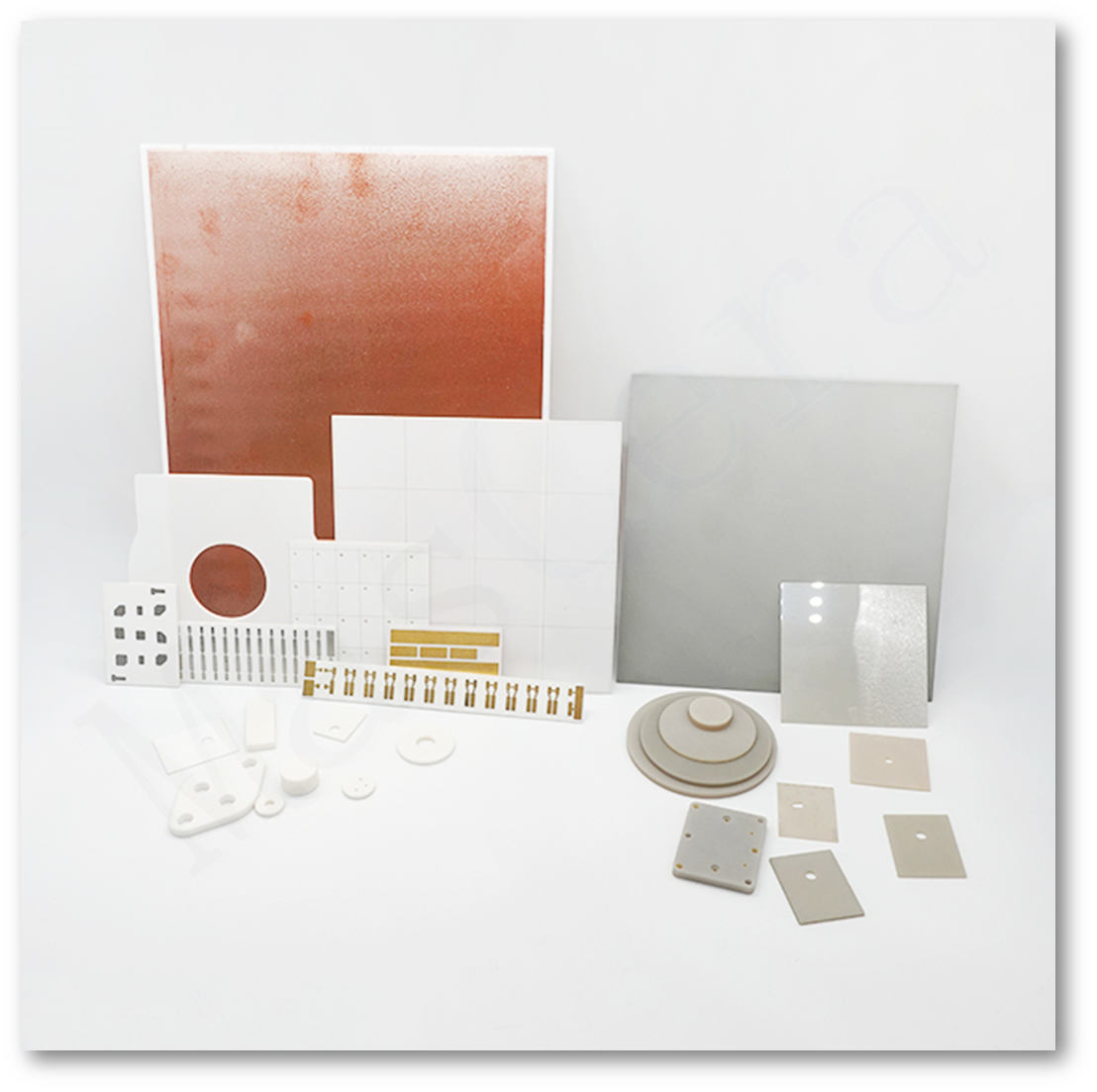
Applications of Alumina Ceramics in LED Technology
The LED industry continues to push boundaries from high-power lighting to advanced displays. Modern trends like solid-state UV sterilization, mini-LED backlighting, and micro-LED displays demand components that can endure high thermal loads and precise fabrication. Traditional materials (like plastics or FR4 circuit boards) often struggle under these conditions – for instance, standard FR4 PCB laminates are not suitable for use with high-power LEDs due to poor heat dissipation. This is where alumina ceramic components come into play. This is where alumina ceramic components come into play. Engineers increasingly turn to alumina ceramic for LED applications because this advanced ceramic offers a combination of high thermal stability, excellent electrical insulation, and mechanical durability unmatched by conventional materials. The following sections discuss why alumina (Al₂O₃) is a material of choice in LED technology and explore the major applications of alumina ceramic components across the industry.
Why Alumina Ceramic is Used in LED Technology
Alumina ceramic (aluminum oxide) has a unique blend of properties that make it ideal for LED technology.
First, it is an electrically insulating but thermally conductive material. Unlike metal-core boards or FR4, alumina can carry heat away from LED chips while electrically isolating them – a critical feature for LED modules. Typical 96% alumina substrates have a thermal conductivity around 24 W/m·K , vastly higher than epoxy PCB materials, though lower than more exotic ceramics like AlN. This thermal performance allows alumina substrates to dissipate heat directly, without additional thermal barriers,improving LED lifetimes and reliability. Alumina also offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability, remaining far more heat-resistant than any temperature encountered in LED operation.
Another key advantage is dimensional stability and low coefficient of thermal expansion. Alumina’s CTE (~7–8 ppm/°C) is lower than many metals and plastics,meaning it expands less with temperature changes. This reduces stress on LED dies and solder joints during thermal cycling. As a result, alumina packages and boards help prevent cracking or delamination in LED assemblies. Alumina is also chemically inert and moisture-resistant, so it won’t corrode or absorb water over time, even in humid or outdoor environments. Unlike polymer components, ceramic won’t discolor or degrade under intense UV light or blue wavelengths.
In terms of cost and manufacturing, alumina ceramics offer better cost-performance than materials like AlN, with mature processing methods suitable for mass production. They can be formed into complex shapes through processes such as tape casting and thick-film metallization. Therefore, alumina has become the most widely used ceramic material for LED component applications.
Major Applications of Alumina Ceramic Components in LEDs
Alumina is one of the most common ceramics in LED packaging, used as the substrate for SMD LEDs, COB arrays, and other high-power modules. It provides a stable platform for chip mounting, electrical insulation, and efficient heat spreading, making it suitable for IR, UV, and UV-C devices. Unlike plastics that carbonize under deep-UV light, alumina remains stable and can be finished with a white reflective coating to boost optical output.
Many mid- and high-power LED packages—such as 3535 and 5050—use white alumina bases that act as both the reflective cavity and structural housing, enabling higher drive currents. Mini-LED backlight units also depend on alumina substrates to manage heat in dense chip arrays.
Overall, alumina ceramic substrates form the core structure of modern LED components, supporting reliable electrical insulation, thermal performance, and long-term stability across a wide range of LED architectures.
Alumina ceramics are widely used as LED cavities and housings because they offer high reflectivity, strong UV stability, and excellent heat resistance. Unlike plastic parts that can yellow or deform, alumina maintains a bright, reflective surface even under high junction temperatures.
High-power LEDs—such as those used in automotive lighting, stage lamps, and multi-chip modules—often rely on alumina housings to keep optical performance stable through reflow soldering and thermal cycling. Its chemical inertness and mechanical strength ensure long-term reliability and consistent light output in demanding LED applications.
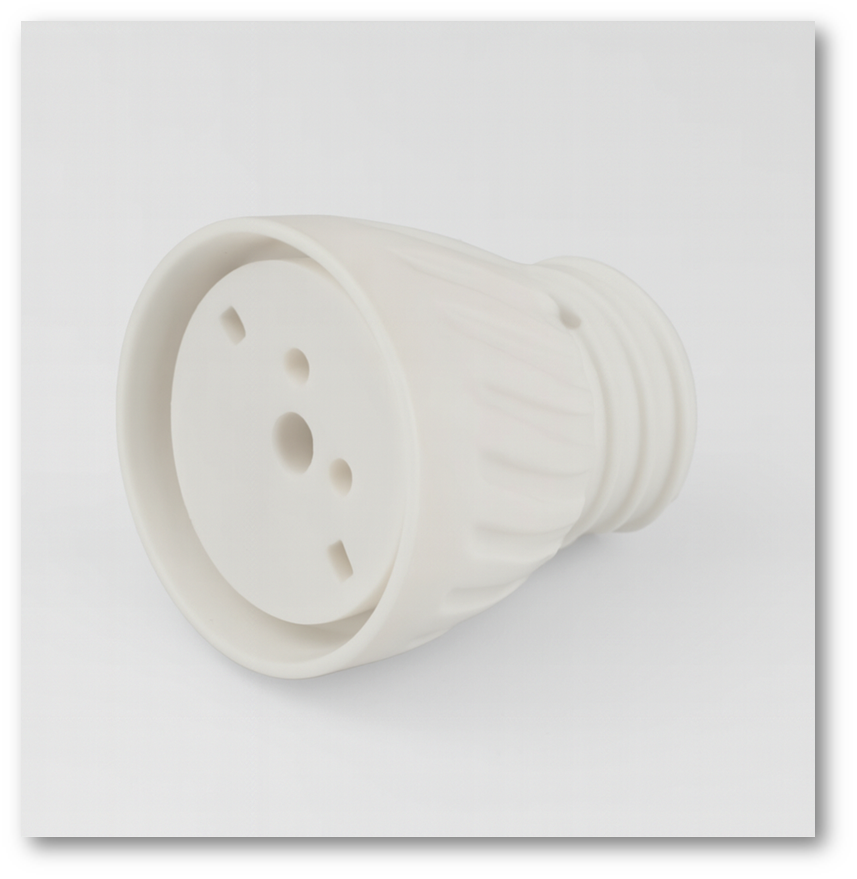
3.Ceramic Holders and Packages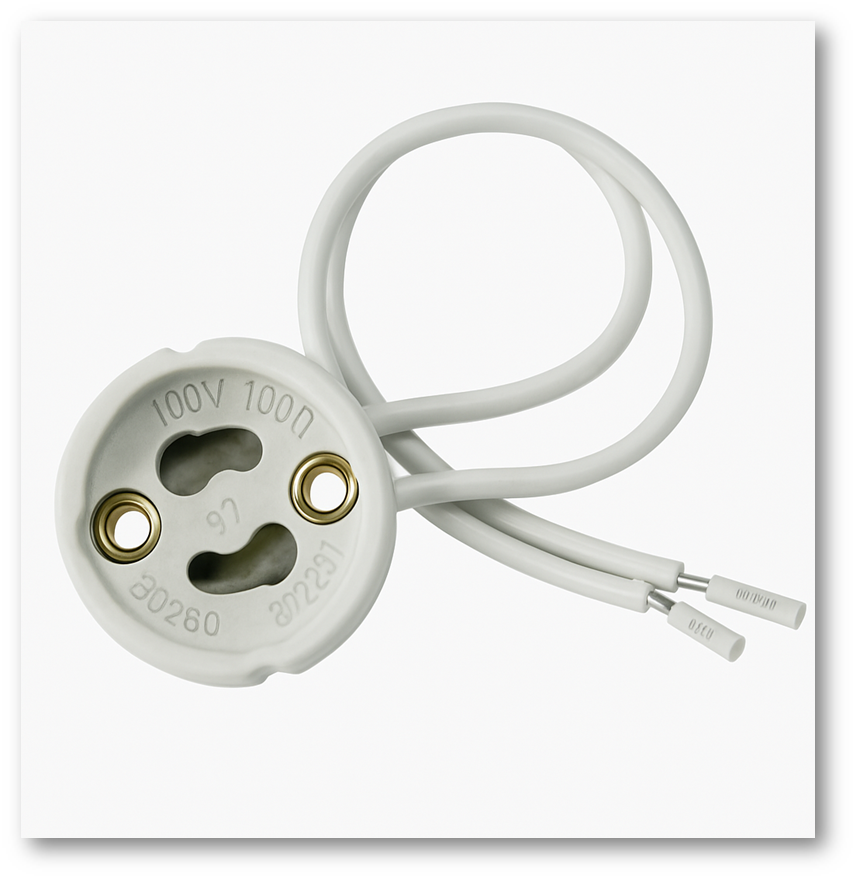
Alumina ceramics are widely used as structural holders and package bodies in LED lamps and modules. Traditional lamp bases such as GU10 and MR16 use ceramic sockets for heat resistance, and the same materials remain common in LED retrofit designs. In COB LEDs, the package may be a full alumina ring or plate with metal pads for chip mounting, offering mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and reliable performance under high power. Many high-power LED series, such as Osram Ostar and Oslon, use ceramic packages to achieve superior heat resistance compared with plastic housings.
Ceramic holders are also used in COB clamps, LED fixture hardware, and mounting accessories like spacers and alignment parts. Whenever a component must resist heat, provide insulation, and maintain structural rigidity, alumina is a preferred choice. These ceramic parts help ensure long-term safety, stability, and electrical isolation in LED systems.
4.Insulation Sheets and Spacers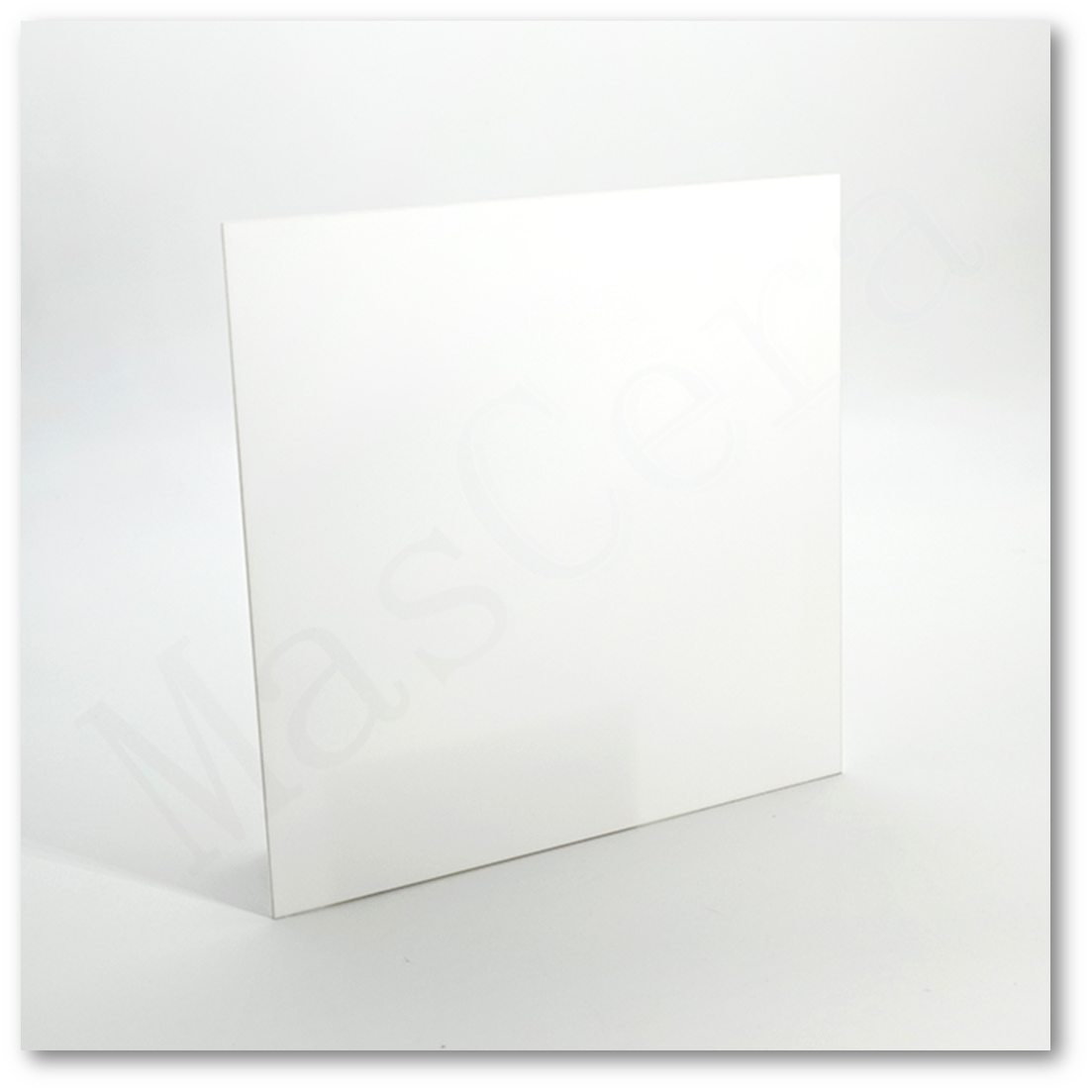
LED assemblies often require thin insulating pads or spacers that provide electrical isolation while conducting heat. Alumina ceramic sheets (typically 0.5–1 mm) can replace silicone or mica pads, offering far higher thermal conductivity and stable dielectric strength without aging or oil migration.
Ceramic spacers and standoffs—such as small posts, rings, or washers—are used on LED PCBs and lamp assemblies to prevent short circuits and support precise mechanical alignment. They maintain tight tolerances, withstand high temperatures, and avoid the parasitic effects common in plastics. As a result, alumina spacers are widely adopted in high-power, high-voltage, and high-frequency LED products.
5.Ceramic Heat Spreaders and Thermal Pads
Alumina ceramics are widely used as heat spreaders and thermal pads in LED systems, especially for COB modules, UV LEDs, and LED drivers. Thin alumina pads—often in TO-220 style—provide electrical insulation while efficiently transferring heat from power devices to heatsinks. Compared with silicone or mica pads, ceramic pads are thinner, more stable, and offer lower thermal resistance.
Alumina plates also serve as baseplates for COB LEDs, distributing heat and providing a rigid mounting surface. Because the ceramic itself is the dielectric, it enables direct heat conduction to metal heatsinks, a principle used in DBC-style substrates. Overall, alumina heat spreaders are key where electrical isolation and thermal management must coexist in compact LED assemblies.
6.Alignment Plates in Mini/Micro-LED
Mini-LED and micro-LED production relies on precision alignment plates to position thousands of tiny LED chips. Ceramic versions—made from alumina or zirconia—offer superior rigidity, thermal stability, and dimensional accuracy compared with engineering plastics. Their laser-machined holes match pixel pitch and remain stable even under thermal cycling, ensuring precise chip placement.
Ceramic materials are also used for related tooling such as pick-and-place nozzle tips and vacuum chucks, providing hardness, cleanliness, and long-term stability required for micron-scale assembly processes.
7.Optical Structural Components
Alumina ceramics are used in optical and mechanical structures inside LED systems, including baffles, light shields, lens holders, and sensor mounts. These components withstand high temperatures, maintain alignment, and do not deform like plastics. In high-intensity projectors, UV curing lamps, or IR sensing modules, ceramic parts ensure stable optical paths and secure mechanical support. Their heat resistance, insulating properties, and dimensional stability make them ideal for demanding optical environments.
Alumina ceramics provide the thermal stability, electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and cost balance needed for modern LED technology. Alumina meets most LED requirements at a far lower cost. Its broad use—from substrates and housings to spacers and optical components—demonstrates its versatility.As LED systems continue to shrink and intensify, alumina will remain a foundational material enabling reliable, long-life, and high-performance lighting and display solutions.






