How strong is alumina ceramic?
How Strong Is Alumina Ceramic?
Alumina ceramic is widely recognized as a hard and durable engineering material, especially in applications where wear resistance, surface stability, and long-term reliability are required. However, the question “how strong is alumina ceramic” is often misunderstood, particularly when strength is interpreted using the same criteria applied to metals.
In ceramic engineering, strength does not describe a single property or a simple numerical value. Instead, it reflects how a material responds to different types of mechanical loading and how it fails under stress. To correctly evaluate whether alumina ceramic is suitable for a given application, it is essential to understand what “strength” means in a ceramic context, how it differs from hardness, and what limitations must be considered during design.
What Does “Strength” Mean in Alumina Ceramics?
In engineering terms, strength refers to a material’s ability to withstand applied loads without fracture. For alumina ceramics, this concept differs fundamentally from metals due to their brittle fracture behavior. Unlike metals, alumina ceramics exhibit almost no plastic deformation. As a result, tensile strength is rarely used as a primary design parameter. nstead, mechanical performance is typically assessed through flexural strength and compressive strength, which better represent how ceramic components behave under realistic service conditions.
In practice, flexural strength is often used as a reference because it reflects how alumina components fail under bending stresses commonly encountered in industrial applications. When alumina ceramic is described as “strong,” it usually refers to reliable resistance to bending and compression rather than the ability to stretch or absorb impact energy.
Strength vs Hardness in Alumina Ceramics
Strength and hardness are frequently used interchangeably when describing alumina ceramics, but they represent different aspects of material behavior. Strength describes resistance to overall mechanical loading, such as bending or compression, without fracture. Hardness, in contrast, refers to resistance to localized surface deformation, including indentation, scratching, and abrasive wear.
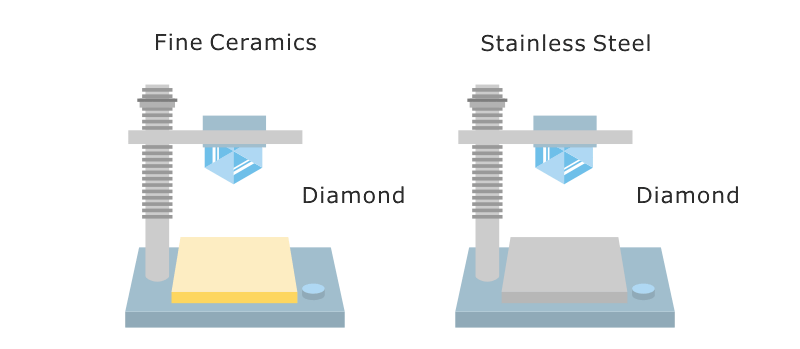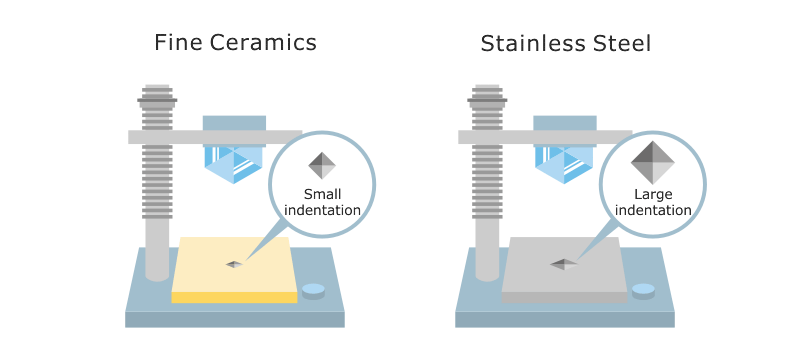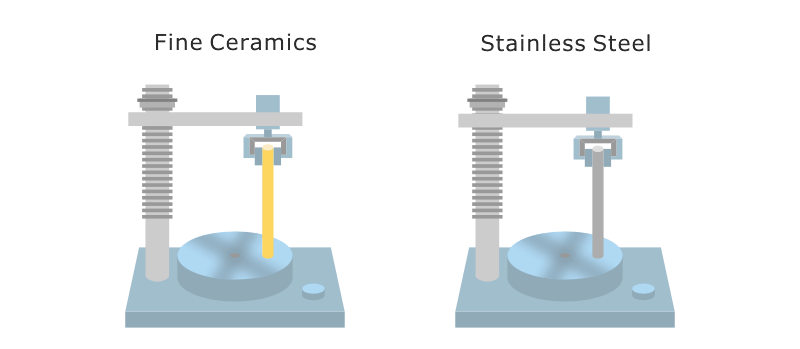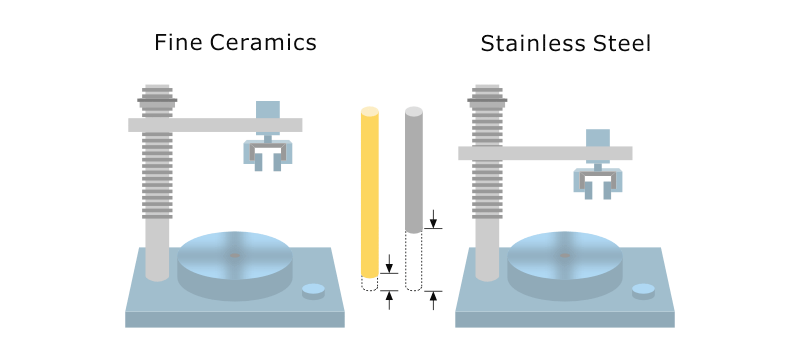
(Image adapted from Kyocera)
Alumina ceramics are widely regarded as “strong” largely because of their very high hardness and excellent wear resistance. However, despite their hardness, alumina ceramics remain brittle materials and do not tolerate impact or tensile stress in the same way as metals. Correctly distinguishing between strength and hardness is essential for interpreting performance data and avoiding incorrect material selection.
Typical Strength Characteristics of Alumina Ceramic
Alumina ceramics exhibit a combination of mechanical characteristics that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. They generally show high compressive strength, good resistance to bending stresses, and stable mechanical behavior under steady loading conditions. At the same time, alumina ceramics have limited tolerance for tensile stress and impact loading. Failure typically occurs through brittle fracture initiated at surface flaws or internal defects rather than gradual yielding. Rather than relying on a single strength value, engineers evaluate alumina ceramics based on how these characteristics interact under the expected service environment.
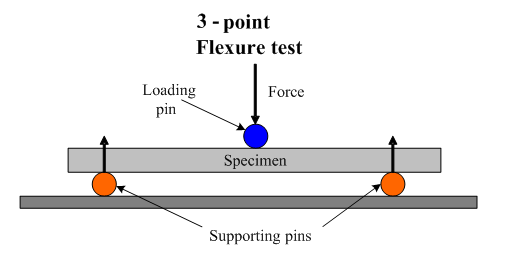
How Microstructure and Purity Influence Strength
The mechanical strength of alumina ceramic is strongly influenced by its microstructure and material purity. Factors such as grain size distribution, porosity, and the presence of secondary phases all affect how stresses are distributed within the material.
A dense, uniform microstructure with fine and consistent grains generally results in improved mechanical reliability. Reduced porosity minimizes stress concentration points, which can otherwise serve as crack initiation sites. Material purity also plays a role by limiting impurities that may weaken grain boundaries or disrupt microstructural uniformity.
It is important to note that increasing purity alone does not automatically guarantee higher strength. Optimized processing and microstructural control are equally important in achieving consistent mechanical performance.
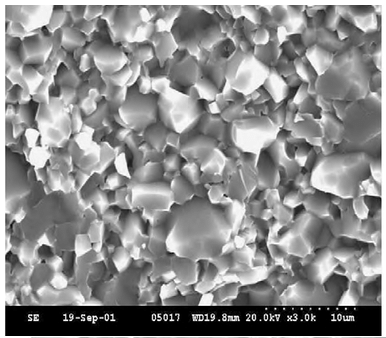
Design Considerations: When Strength Is Not the Limiting Factor
In many alumina ceramic applications, failure is not caused by insufficient material strength but by external factors related to design and operating conditions.Thermal shock, improper mounting, sharp corners, and uneven load distribution can all introduce stresses that exceed the material’s tolerance. Because alumina ceramics are brittle, they are particularly sensitive to stress concentrations and rapid temperature changes.Effective design strategies—such as smooth geometry transitions, appropriate tolerances, and controlled assembly methods—are often more critical to component reliability than selecting a material with marginally higher strength.
How Alumina Ceramic Compares to Other Technical Ceramics
When compared to other technical ceramics, alumina ceramic offers a well-balanced combination of strength, hardness, electrical insulation, and chemical stability. Some ceramics, such as zirconia, provide higher fracture toughness, while others, such as silicon nitride, may offer superior strength retention at elevated temperatures.
Alumina remains a widely used choice because it delivers reliable mechanical performance across a broad range of applications without the complexity or cost associated with more specialized ceramic materials.
Interpreting Strength in Real Applications
Alumina ceramic is a strong engineering material when strength is interpreted correctly. Its high compressive and flexural strength, combined with excellent hardness and wear resistance, make it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
However, strength alone does not define performance. Successful use of alumina ceramic depends on understanding the difference between strength and hardness, recognizing the role of microstructure and purity, and applying sound engineering design principles. When these factors are properly considered, alumina ceramic can deliver long-term reliability in a wide range of applications.
>> For a broader overview of alumina ceramic properties and applications, please refer to our main alumina ceramic guide.
Alumina Ceramic Products To support practical design and manufacturing needs, Mascera offers a comprehensive range of alumina ceramic products, including standard shapes and custom-engineered components. Our product portfolio covers substrates, tubes, rods, plates, and wear parts designed for electronic, thermal, and mechanical applications.
🔗 Explore our alumina ceramic product range




