Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)

Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), commonly known as alumina ceramic, is one of the most widely used and most cost-effective technical ceramics.Its combination of mechanical strength, high hardness, thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance makes it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Mascera supplies alumina ceramics in multiple purities (95%–99.8%) and customizes precision components for applications in photovoltaics, electronics,machinery,textile equipment,automotive,semiconductor processing,medical devices,and high-temperature furnace systems.
Properties
High hardness
High mechanical strength
Outstanding wear resistance
High temperature resistant
Good electrical insulation
Low dielectric constant
Good acid & alkali resistance
Properties Data
| ltem | Unit | 95% Al2O3 | 96% Al2O3 | 99% Al2O3 | 99.5% Al2O3 | 99.7% Al2O3 | 99.8% Al2O3 |
| Purity | % | 95 | 96 | 99 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| Color | - | White/Pink | White | lvory | lvory | lvory | lvory |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.65 | 3.72 | 3.85 | 3.90 | 3.92 | 3.92 |
| HV Hardness | - | >1300 | >1300 | 1700 | 1750 | 1800 | 1800 |
| Fracture Toughness | Mpa.m½ | 3-4 | 3-4 | 3-4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Young's modulus | Gpa | 320 | 330 | 340 | 370 | 380 | 390 |
| Flexural Strength@25°C | Mpa | 300 | 300 | 330 | 375 | 380 | 390 |
| Compressive Strength@25°C | Mpa | 2200 | 2200 | 2350 | 2450 | 2480 | 2500 |
| Thermal Conductivity@25°C | W/m.k | 18-22 | ≥24 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 32 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient(25-1000°C) | 10-⒍mm/°C | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | ∆T(°C) | 220 | 220 | 180-200 | 180-200 | 180-200 | 180-200 |
| Max. Working Temperature | °C | 1500 | 1500 | 1650 | 1700 | 1700 | 1700 |
| Dielectric Strength | kv/mm | 16 | 17.2 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Electrical Resistivity@25°C | Ω.cm | 1014 | 1014 | 1014 | 1014 | 1014 | 1014 |
Dielectric Constant (@1MHz, 25°C) | - | 9 | 9 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 9.8 |
Dielectric Loss (@1MHz, 25°C) | - | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
Note: above data is for reference only, the values may vary according to product configuration, geometry and manufacturing process.
Applications
Alumina ceramic is widely used across industries due to its balanced performance and cost efficiency. Typical applications include:
Seal rings for pumps
Plungers or pistons for valves
Electronic ceramic substrates
Thermocouple protection tubes
Textile eyelets or guides
Electrical insulators
Heat resistant ceramic crucibles
Ceramic parts for high temperature furnace
Mascera Manufacturing Capabilities
Mascera specializes in precision manufacturing of alumina ceramic components, providing stable quality and flexible lead times based on part complexity and production processes.
Manufacturing processes include:
Forming processes:Dry pressing / Isostatic pressing / Hot pressing / Tape casting / Injection molding / Slip casting
Precision machining:CNC grinding, lapping, and fine polishing
Laser processing:Laser drilling / Laser scribing / Laser cutting / Laser marking
Post-processing:Glazing and metallization
Dimensional capability:
Actual tolerances depend on material grade, part geometry, and machining process.
Linear tolerance: achievable down to ±0.002 mm
Angular tolerance: achievable down to ±0°10′
Surface roughness: as low as Ra 0.05 μm for suitable surfaces
Concentricity, cylindricity, flatness, parallelism, straightness: achievable down to 0.02 mm
Minimum hole diameter: 0.5 mm (depending on thickness and aspect ratio)
Internal thread minimum: M2; external thread maximum: M20
Production support:
Material traceability and COA/COC
Prototype to mass production
Engineering support for design optimization
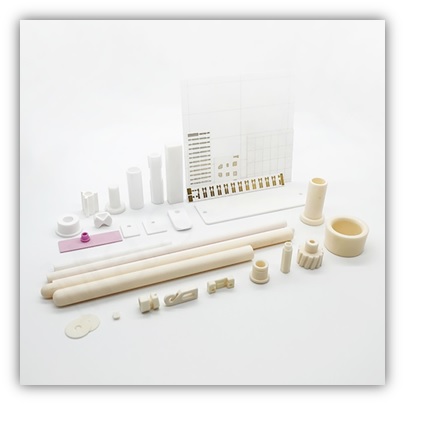
Custom Alumina Ceramic Components
Mascera provides customed alumina ceramic parts according to drawings, 3D models or functional requirements.Supported product categories include:
Why Choose Mascera
Over 10 years of experience in technical ceramic manufacturing
Full range of alumina purity grades to match cost and performance
Strong machining capability for both simple and complex parts
Strict quality control and complete inspection records
Fast response, fast sampling, stable mass production
Global supply to electronics, machinery, power equipment, medical, and research institutions
FAQ
Q1: What purity of alumina should I choose?
The choice of alumina purity depends on the performance requirements of your application.
Below is a general guideline based on common industrial usage:
95% and 99% alumina
The most widely used grades for general structural components.They offer good mechanical strength and wear resistance at an economical cost.96% and 99.6% alumina
Commonly used for ceramic substrates and electrical insulation sheets due to their stable dielectric properties.99.5% alumina
Typically selected for high-temperature tubes and rods,providing higher density and improved thermal resistance.99.7% and above
Preferred for precision structural parts and high-end applications, where extremely low impurities and excellent electrical insulation are required.
If you are unsure which purity is suitable, you are always welcome to consult us for recommendations based on your specific application.
Q2: Do alumina ceramics have good thermal shock resistance?
Alumina ceramics offer moderate thermal shock resistance, but they are not the ideal choice for applications involving rapid temperature changes.
The actual performance depends on purity, geometry, and heating/cooling rate.
In general:
Lower-purity alumina (95%) has slightly better thermal shock resistance due to higher porosity.
High-purity alumina (99% and above) is denser and stronger, but more sensitive to sudden temperature fluctuations.
Therefore, if alumina is used in a high-temperature application, please provide the heating and cooling rates so we can evaluate whether alumina is suitable for your operating conditions.
Q3: Can Mascera produce small batch prototypes?
Yes, we support rapid sampling from a few pieces to mass production.
Q4: Can alumina replace metal components?
Alumina ceramics can replace metal components in applications that require electrical insulation, high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or stability at elevated temperatures.In such environments, alumina often performs better than metals because it does not conduct electricity, maintains hardness at high temperatures, and resists chemical attack.
However, alumina is more brittle than metals and may not be suitable for applications involving impact, shock loads, or bending forces.If you are considering replacing a metal part with alumina, feel free to consult us so we can evaluate suitability based on your working conditions.