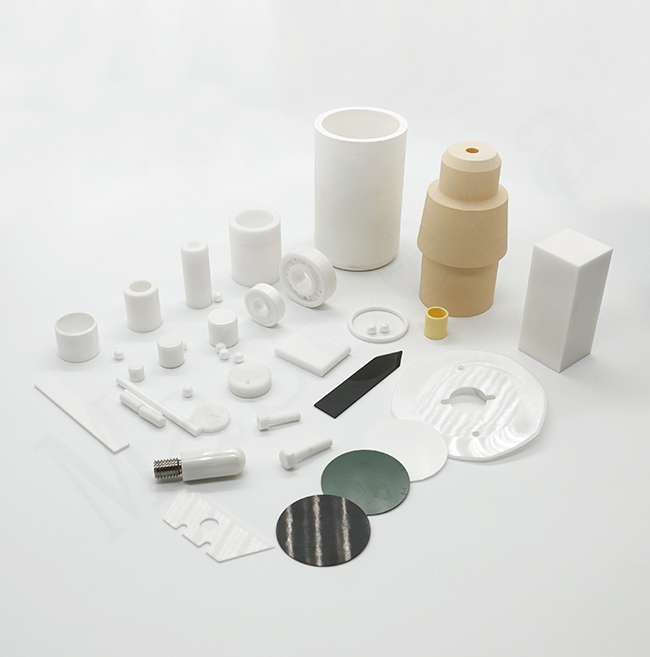
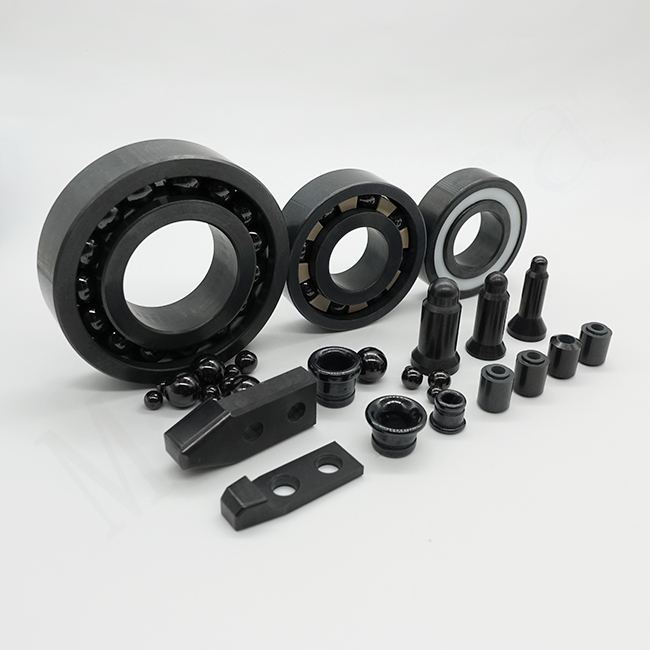
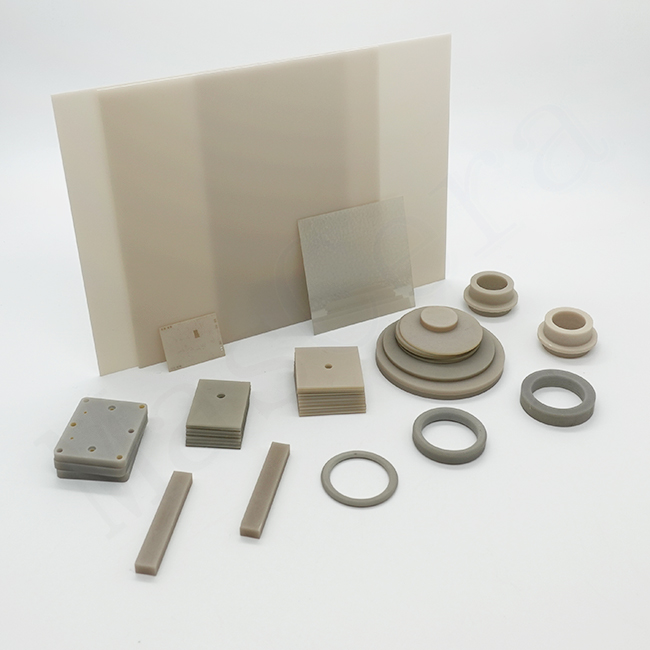
Technical Ceramics
Technical ceramics, also known as engineering ceramics or advanced ceramics, are high-performance ceramic materials specifically developed for demanding industrial, electronic, and high-temperature applications. Unlike traditional ceramics used for decorative or structural purposes, technical ceramics are engineered to provide exceptional mechanical strength, thermal stability, electrical insulation, wear resistance, and chemical durability under extreme operating conditions.
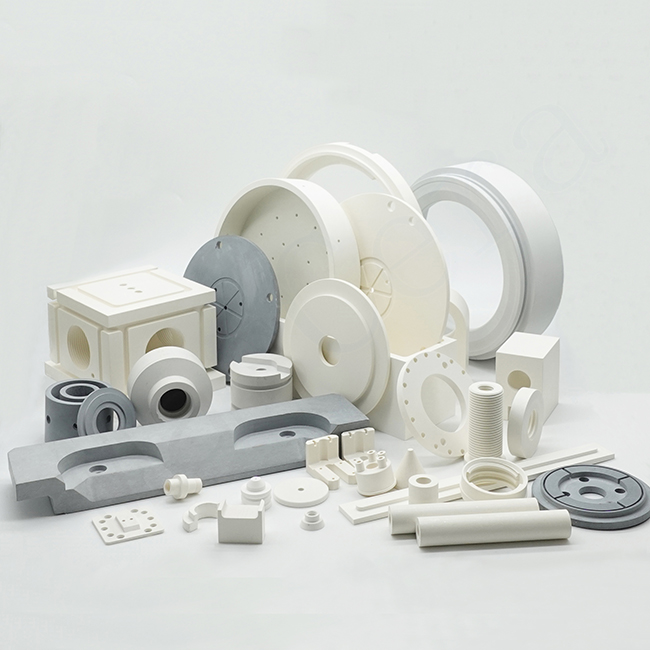
As a professional technical ceramics manufacturer, Mascera specializes in the custom manufacturing and precision machining of advanced ceramic components made from Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), Silicon Carbide (SiC), and Boron Nitride (BN). Our technical ceramics are widely applied in power electronics, semiconductor equipment, automotive systems, industrial machinery, and high-temperature processing environments.
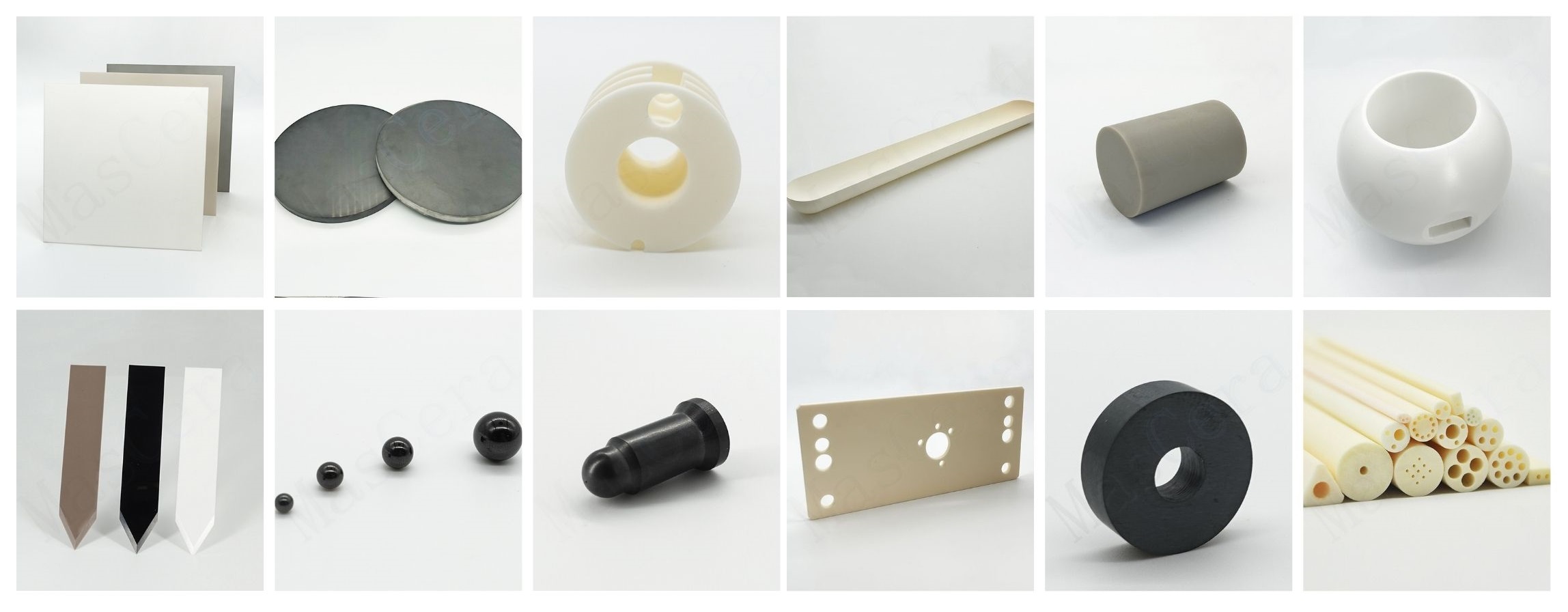

What Are Technical Ceramics?
Technical ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials processed through precisely controlled powder preparation, forming, and high-temperature sintering processes to achieve superior material properties. These ceramics are engineered for performance rather than appearance.
Compared with conventional ceramics:
• Higher mechanical strength
• Greater hardness and wear resistance
• Improved fracture toughness
• Excellent thermal and electrical performance
• Superior resistance to corrosion and oxidation
Because of these characteristics, technical ceramics have become indispensable in modern industrial systems where metals or polymers cannot meet performance requirements.
Key Properties of Technical Ceramics
Mechanical Properties
Technical ceramics exhibit extremely high hardness and compressive strength. Materials such as Alumina and Silicon Carbide provide excellent wear resistance, making them ideal for sliding components, seals, bearings, and abrasive environments. Zirconia offers enhanced fracture toughness compared to many other ceramic materials, enabling improved resistance to mechanical shock and impact.
Key mechanical advantages include:
• High hardness
• Superior compressive strength
• Excellent wear resistance
• Low deformation under load
• High dimensional stability
Thermal Properties
One of the defining characteristics of technical ceramics is their ability to maintain performance at elevated temperatures.
• Alumina and Silicon Carbide withstand temperatures above 1600°C
• Silicon Nitride provides strong thermal shock resistance
• Aluminum Nitride offers high thermal conductivity combined with electrical insulation
• Boron Nitride exhibits thermal stability with low thermal expansion
These properties make technical ceramics ideal for furnace components, thermal management systems, heating elements, and semiconductor processing equipment.
Electrical Properties
Many technical ceramics provide outstanding electrical insulation performance.
• High dielectric strength
• High volume resistivity
• Low dielectric loss
• Stable insulation at high temperatures
Aluminum Nitride uniquely combines electrical insulation with high thermal conductivity, making it widely used in power electronics and LED substrates.
Chemical & Environmental Resistance
Technical ceramics are highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation, acids, and alkalis.
• Excellent chemical inertness
• Strong oxidation resistance
• Stable performance in harsh environments
• Radiation resistance for specialized applications
These properties allow technical ceramics to operate reliably in chemical processing, vacuum systems, and aggressive industrial environments.
Classification of Technical Ceramic
Materials Mascera provides advanced technical ceramics based on six major material systems:
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
A cost-effective ceramic with excellent hardness, electrical insulation, and wear resistance.
Zirconium Oxide(ZrO2)
High fracture toughness and strength, ideal for structural and wear-resistant applications.

Hot-Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN)
Machinable ceramic with excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation, used in high-temperature vacuum or inert gas conditions.
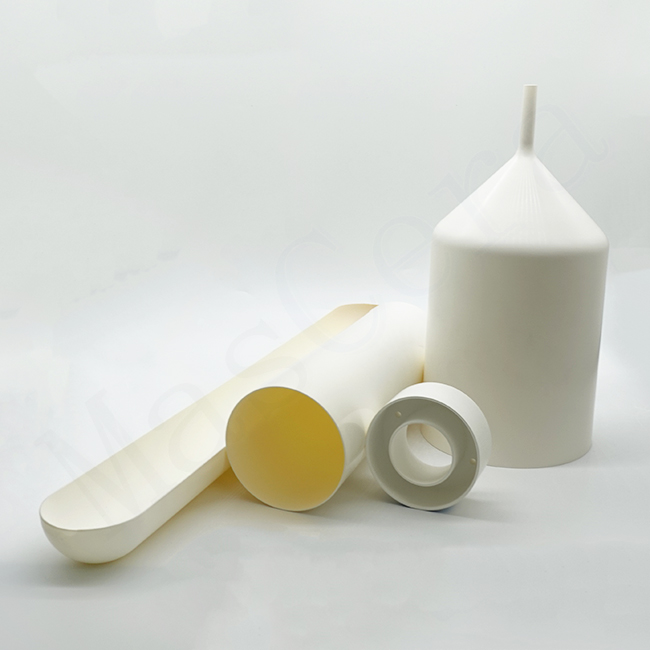

Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN)
Ultra-pure and non-wetting to molten metals, ideal for semiconductor crystal growth and high-vacuum applications.
Silicon Nitride (Si3N4)
One of the strongest technical ceramics with superior mechanical properties and excellent thermal shock resistance.
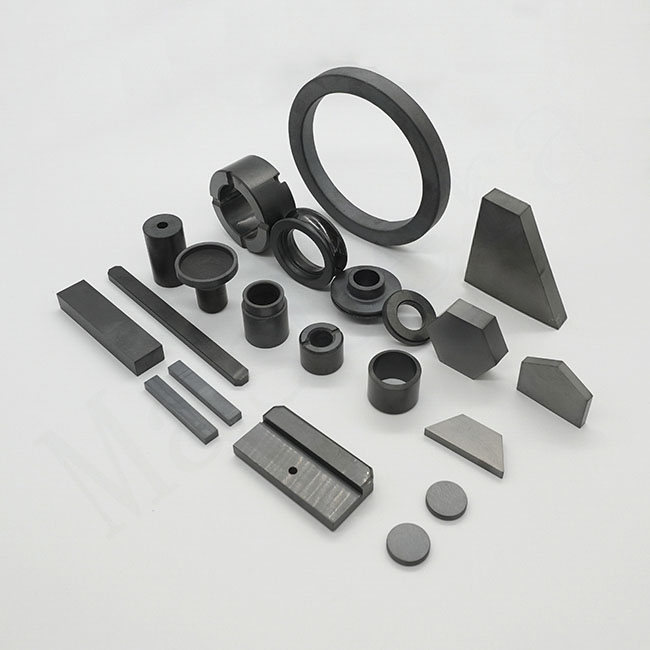

Silicon Carbide (SIC)
Extremely hard and thermally conductive; SSiC and RBSiC are ideal for harsh, high-temperature, and chemically corrosive environments.
Combines high thermal conductivity with excellent electrical insulation, making it perfect for electronic substrates and heat dissipation modules.
Applications of Technical Ceramics
Technical ceramics play a critical role in modern industrial systems where extreme temperature, electrical insulation, wear resistance, and dimensional stability are required. Their unique combination of mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties enables reliable performance in demanding environments where conventional materials fail.
Below are the major industries where advanced technical ceramics are widely applied.
Power Electronics & Thermal Management
In power electronics systems, effective thermal dissipation and electrical insulation are essential for long-term reliability and performance stability. Technical ceramics such as Aluminum Nitride (AlN) and high-purity Alumina are commonly used as substrates, insulating plates, and heat dissipation components due to their excellent dielectric strength and high thermal conductivity.Ceramic substrates provide electrical isolation between conductive layers while efficiently transferring heat away from power devices such as IGBTs, MOSFET modules, and LED systems. Their low thermal expansion and dimensional stability ensure minimal stress under repeated thermal cycling.
Typical applications include:
• Power module substrates
• Insulating washers and spacers
• Ceramic heat spreaders
• LED base plates
• High-voltage insulating components
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• Aluminum Nitride (AlN)– high thermal conductivity with electrical insulation
• Alumina (Al₂O₃) – cost-effective insulating substrate material
Semiconductor Equipment
Semiconductor manufacturing environments demand extreme cleanliness, precision, and temperature resistance. Technical ceramics are widely used in wafer processing systems, etching equipment, plasma chambers, and vacuum handling assemblies due to their high purity and resistance to chemical corrosion.Ceramic components ensure dimensional precision, electrical insulation, and chemical stability under plasma and reactive gas exposure.
Typical applications include:
• Wafer handling arms
• Insulating rings
• Chamber liners
• Electrostatic chuck components
• Vacuum insulation parts
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• High-Purity Alumina– excellent insulation and chemical resistance
• Silicon Carbide (SiC) – plasma resistance and high temperature stability
• Boron Nitride (BN) – specialized thermal processing components
Automotive Systems
Modern automotive systems increasingly rely on advanced technical ceramics for durability and performance under high temperature and mechanical stress. Silicon Nitride and Zirconia are frequently used in applications requiring wear resistance, thermal shock resistance, and mechanical reliability.Technical ceramics improve system efficiency, reduce friction, and enhance service life in demanding engine and sensor environments.
Typical automotive applications include:
• Oxygen sensor components
• Turbocharger parts
• Ceramic bearings
• Wear-resistant valve components
• High-temperature insulating parts
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)– thermal shock resistance and strength
• Alumina (Al₂O₃) – electrical insulation components
Industrial Machinery & Wear Components
Industrial machinery operates under severe wear, high load, and abrasive environments. Technical ceramics offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to hardened steel in many applications.Alumina, Silicon Carbide, and Zirconia are widely used in sealing systems, pumps, and sliding components due to their low friction and corrosion resistance.
Typical applications include:
• Pump plungers
• Mechanical seals
• Valve seats
• Nozzles
• Guide rollers
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• Alumina (Al₂O₃) – wear-resistant structural parts
• Silicon Carbide (SiC)– extreme hardness and abrasion resistance
• Zirconia (ZrO₂)– high-strength precision components
Furnace Systems
In high-temperature processing environments such as metal heat treatment and advanced material sintering, technical ceramics maintain structural integrity where metals would oxidize or deform.Their oxidation resistance, thermal shock resistance, and dimensional stability allow continuous operation at elevated temperatures.
Typical components include:
• Ceramic tubes
• Crucibles
• Furnace rollers
• Support plates
• Insulating structures
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• Silicon Carbide (SiC) – high temperature and oxidation resistance
• Alumina (Al₂O₃) – stable structural components
• Boron Nitride (BN)– non-wetting and thermal shielding applications
Medical & Precision Equipment
High-purity Zirconia and Alumina technical ceramics are used in medical and laboratory systems due to their biocompatibility, wear resistance, and precision machinability.Zirconia’s fracture toughness and chemical stability make it suitable for precision components that require reliability and dimensional accuracy.
Typical uses include:
• Surgical components
• Dental zirconia parts
• Precision dosing pump components
• Laboratory insulation parts
Related Technical Ceramic Materials
• Zirconia (ZrO₂) – biocompatible and high toughness
• Alumina (Al₂O₃) – precision insulation components
Manufacturing & Processing Technologies
High-performance technical ceramics require advanced manufacturing control. Mascera supports:
• Dry pressing
• Isostatic pressing
• Ceramic injection molding
• Slip casting
• High-temperature sintering
• CNC precision machining
• Double-side surface grinding
Precision machining allows tight tolerance control and custom shapes based on customer drawings.
👉 For detailed information about our forming methods, machining capabilities, tolerance control, and metallization processes, please visit our dedicated Manufacturing Capabilities page.
Quality Control
Reliable technical ceramics require strict quality control systems. Mascera implements:
• Incoming raw material inspection
• In-process dimensional verification
• Surface roughness control
• Final inspection
• Traceability system
Our manufacturing process ensures stable performance and dimensional consistency for industrial applications.
👉 For detailed information about inspection equipment, tolerance capability, and quality management procedures, please visit our dedicated Technical Ceramics Quality Assurance page.
Custom Technical Ceramic Components
In addition to standard materials, Mascera specializes in custom technical ceramic components manufactured according to customer drawings.
• OEM production
• Small batch and mass production
• Engineering support
• Precision tolerance control
• Custom metallization and assembly
From prototype to volume production, our technical ceramics are engineered to meet demanding application requirements.
👉 For a detailed overview of how custom ceramic projects are evaluated, confirmed, and processed from quotation to production release, please visit our Technical Ceramic Order Processing Procedure and warranty-policy page.
Technical ceramics represent a critical class of high-performance engineering materials for modern industrial systems. With superior mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties, these advanced ceramic materials enable reliable performance under extreme conditions.
As a dedicated technical ceramics manufacturer, Mascera provides precision-engineered ceramic components based on Alumina, Zirconia, Aluminum Nitride, Silicon Nitride, Silicon Carbide, and Boron Nitride to support global industrial applications.








